From the Editor-in-Chief
Theory and Social Functions of Geography
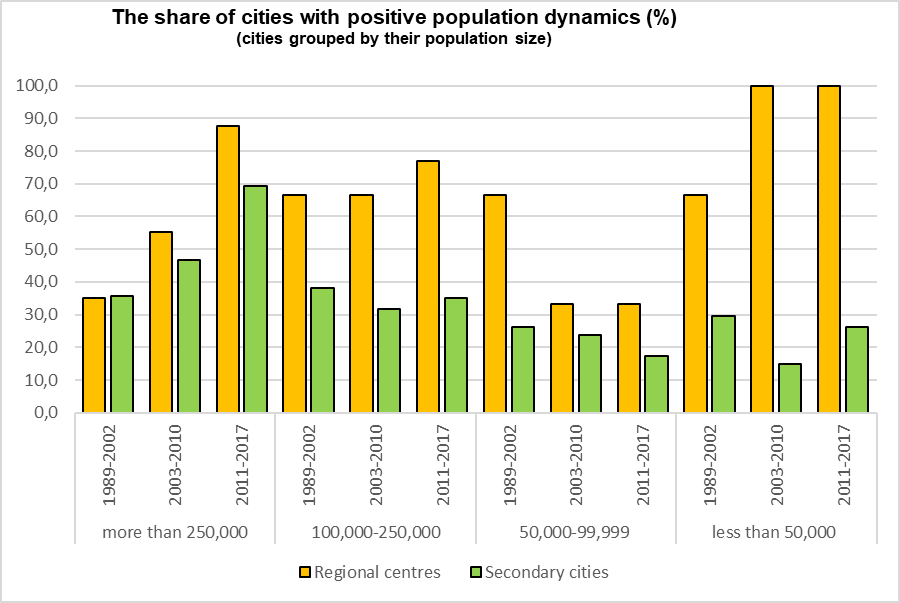
- The decline in natural population growth and dominating centripetal migration strengthen the dominance of the regional centers over the second largest cities.
- In 1959 center’s population was on average 19.1% of the regional one. By 2017 this number has increased to 36.2%. In 2010 in 56 regions the regional centers were at least 3 times larger than the secondary cities.
- The larger gap in population between the regional center and the second city, the higher probability of the growing concentration of population in the regional center.
- Since 2002 the number of regional centers with negative population dynamics has sharply decreased, while the number of second cities with negative population dynamics remains stable.
- The population dynamics in regional centers and second cities does not reveal tendency for the development of polycentricity.
The article analyses the dynamics of the population of 75 regional centers and second by population size cities of the regions in Russia. The analysis is based on the population census data from 1959 to 2010 and on the current recording data for 2011–2017. In the vast majority of regions, there is a significant dominance of the regional center over the second city. It manifests itself both in the absolute parameters of the population size and in the shares of regional centers and second cities in the population sizes of their regions. In 31 regions of the country, the share of the regional center by 2002 already reached 35% and continued to increase. Fifteen years later, in 13 regions of the country, it exceeded 45%. The maximum bar of possible concentration of the population in the regional center is not yet visible. Over time, the prevailing of regional centers over the second cities of the regions is increasing. The analysis showed that the opportunities for population increase in the second cities depend on their population size: gradually, between the second cities with a population of more than 250000 people, the number of growing cities is increasing; between second small cities, the share between depopulating and growing cities is practically unchanged. Thus, the tendencies of centrism in the regions take precedence over polycentricity. The population is increasingly concentrated in separate points, vested with power. These processes are based on historical and evolutionary (history of settlement, development and urbanization), functional-economic, administrative-territorial and demographic determinants. An increasingly important factor contributing to the concentration of the population is institutional factor (associated with the performance by the regional centers of the capital functions and reducing the costs of business and consumers).
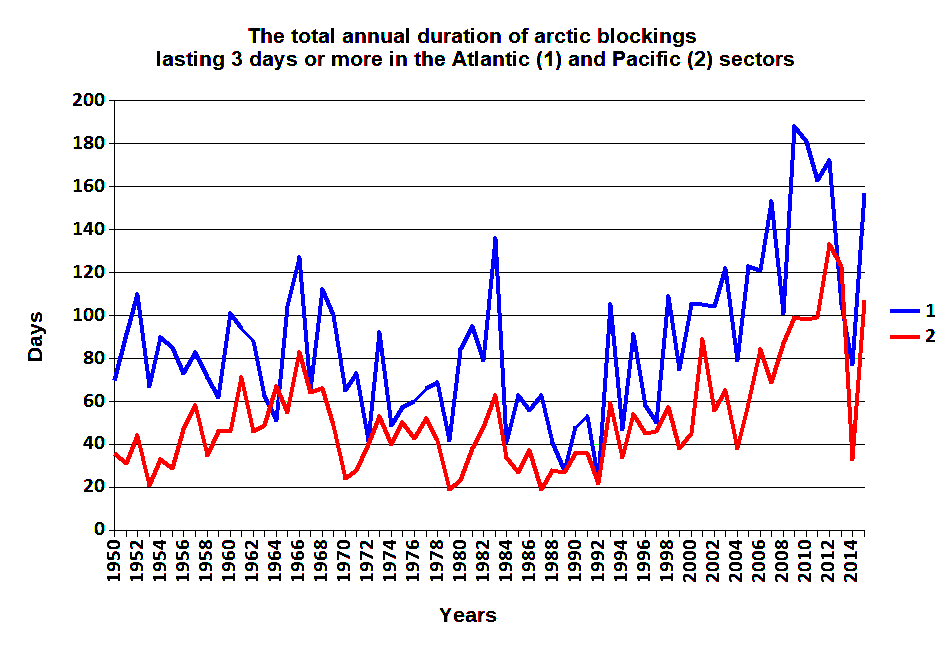
- The statistical relationship of interannual changes in the total duration (TD) of Arctic intrusions with the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in the Pacific sector became in the 21st century less significant than in the 20th century.
- The statistical relationship between TD and ENSO in the Atlantic sector is significant with the time shifts up to 4 months. It is also increasing in the 21st century.
The statistical relationships of interannual changes in the total duration of Long Arctic Invasion in Atlantic and Pacific sectors of the Northern Hemisphere with the formation of baric ridges between the Arctic and subtropical anticyclones with variations of climate indices of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) process are analyzed. Interannual changes in these indices in the 20th century significantly influenced the variations in the total duration of the considered Arctic invasions in the Pacific sector in February. For most indices, this effect was strongest if their ranks, ahead of the ranks of the processes studied for two months. The revealed relationships, in general, are not stationary and vary depending on the period under review. The relationship of ENSO indices and the total duration of the Arctic invasions in the Atlantic sector in November and October are significant in the 21st century, when the time shifts between these processes were 0–4 months.
Territorial Organization of Society
- The hypothesis, that in the absence of standard employment opportunities, population tends to be non-standard, does not work on the example of rural areas of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast (JAO).
- Non-standart employment in the JAO remains in a rudimentary state.
- Rural population prefers employment for agricultural and non-agricultural enterprises.
- 40% of rural population refuses to do business or to get involved in arts and crafts.
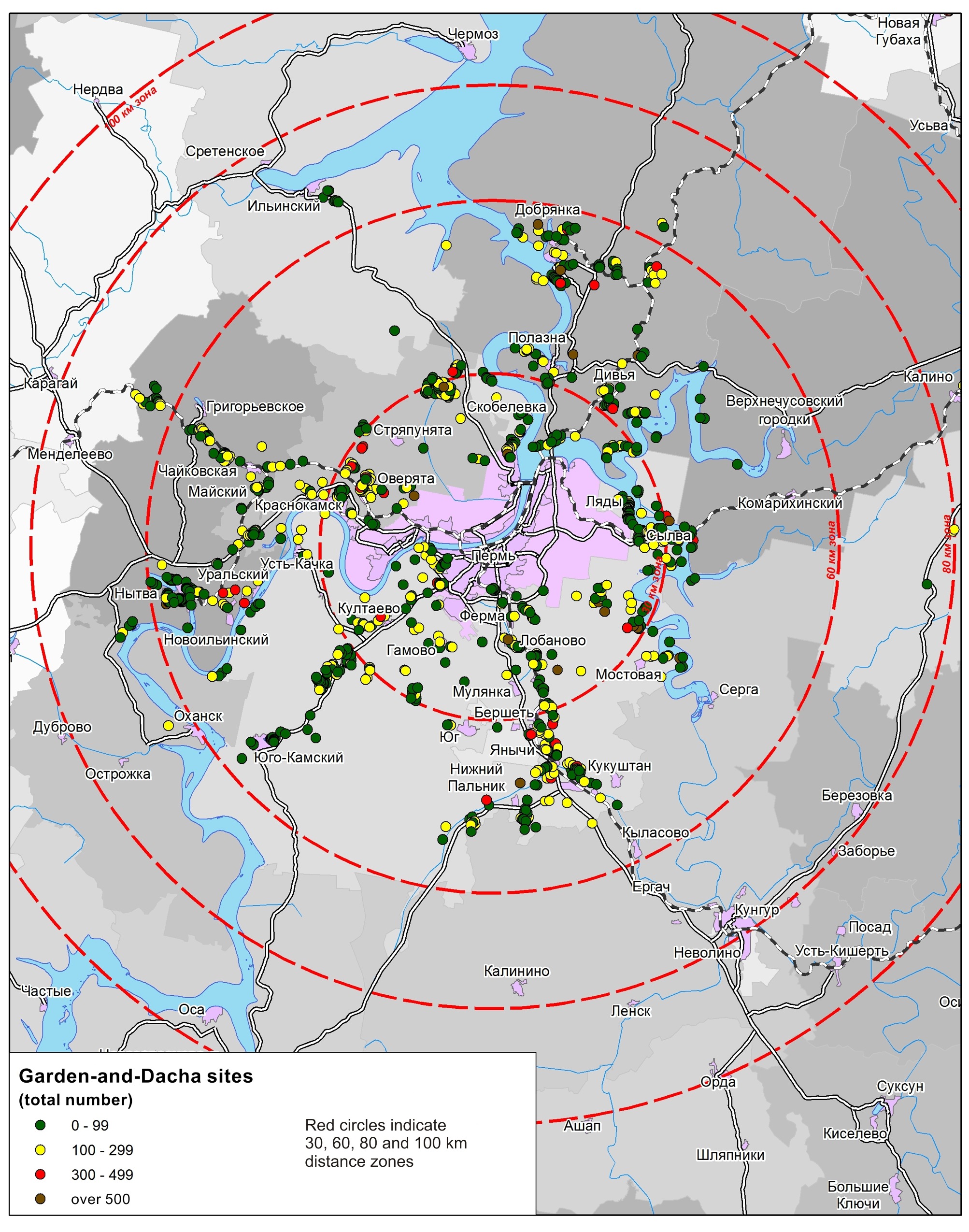
- The use of gardens and dachas by residents of Perm is a recreational tradition of the region.
- Reliable location and quantitative characteristics of garden-and-dacha sites can be found on the Russian public cadastral map.
- Gardens and dachas of the inhabitants of Perm are located within the radius of 60 km from the city.
- Garden-and-dacha sites are located on the territories, which initially had no high recreational potential.
- Gardeners and dacha residents form distinctive territorial communities.
The article presents the results of the study of the collective garden and dacha movement in the suburban area of Perm. The researcher offers a new definition of collective horticulture, gardening and dacha associations of citizens: “garden-dacha formations.” Such collective forms are special associations of people – territorial communities. They exist beyond working hours, within a limited space, mainly outside the urban environment. Such communities are characterized by seasonal activity and have specific interactions with the surrounding territory. The author proposes a methodology for identifying such communities. The study revealed their quantity, distinguishing features, and territorial distribution. The majority of Perm city residents have dachas in suburban Perm municipal district. Other inhabitants of Perm krai own dachas either in Perm municipal district, or in different municipal districts nearby. The various territorial levels of garden and dacha formations reflecting features of their interaction with each other and with the surrounding territory are defined: a site, a garden, an array, a cluster, an area. Factors of spatial distribution for garden and dacha formations across the territory are singled out; their distribution taking into account geographical peculiarities of Perm krai is considered.
Natural Processes and Dynamics of Geosystems
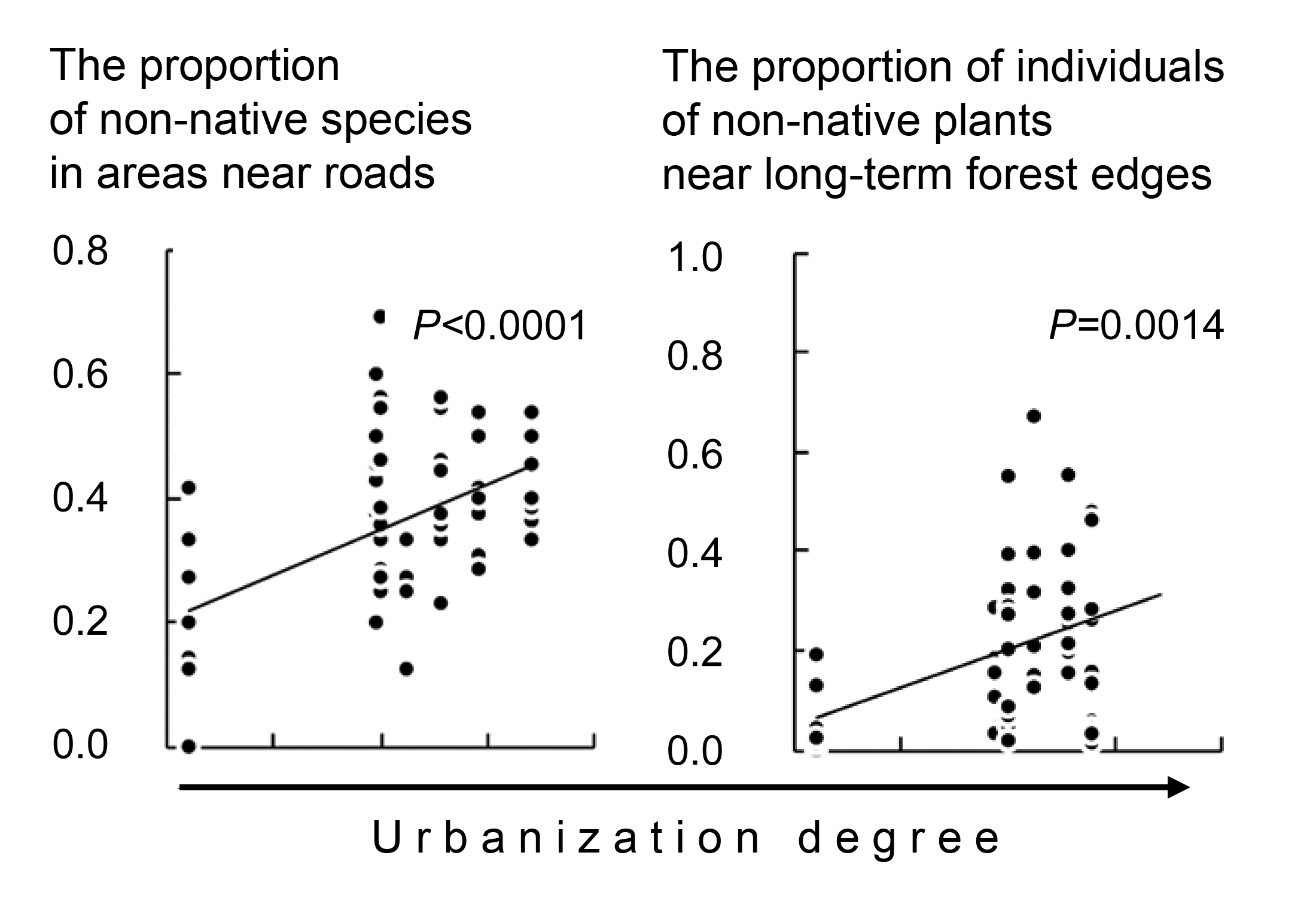
- The main factor of species diversity and abundance of undergrowth vegetation in urban forests is the degree of urbanization, estimated as the distance from the forest plots to the city center and residential buildings.
- An edge effect and the features of the adjacent areas have little effect on the state of the undergrowth vegetation.
- Spatial factors have stronger influence on adventive plants rather than on native ones.
- Species richness and abundance of non-native plants grow with increasing urbanization degree.
The dependence of the understory alien plants distribution in urban forests of Yekaterinburg on such factors as urbanization, habitat fragmentation and structure of forest stands has been studied. Young growth and adult individuals of understory shrubs and trees were registered for 11 transects; 103 descriptions in round plots of 400 square meters have been analyzed. The first hypothesis was that the species richness and abundance of alien plants increased and the species richness and abundance of native plants decreased with the urbanization growth. It was partly confirmed for the statement that the species richness and abundance of alien plants increase with the growth of urbanization. However, the species richness and abundance of native species do not decrease. The second hypothesis is that the species richness and abundance of alien understory trees and shrubs are higher at the boundaries of the urban forests compared to their inner parts. This hypothesis has not been proved. The edge effect proper, implying changes of the understory state in the direction from boundary into the forest stand has not been observed either in the group of native species or in the group of alien species. The third hypothesis is that the species richness and abundance of alien understory trees and shrubs are higher in the urban forest areas adjacent to roads and in the forest stand with long-term boundaries. This hypothesis is partly confirmed. On the one hand, the species richness and abundance of alien understory trees and shrubs are higher in the urban forest areas adjacent to roads compared to areas, adjacent to wastelands. On the other hand, the species richness and abundance of alien understory trees and shrubs are higher in the urban forest areas with recently emerging forest stand boundaries compared to areas with the long-term forest stand boundaries.
Evolution of Natural System
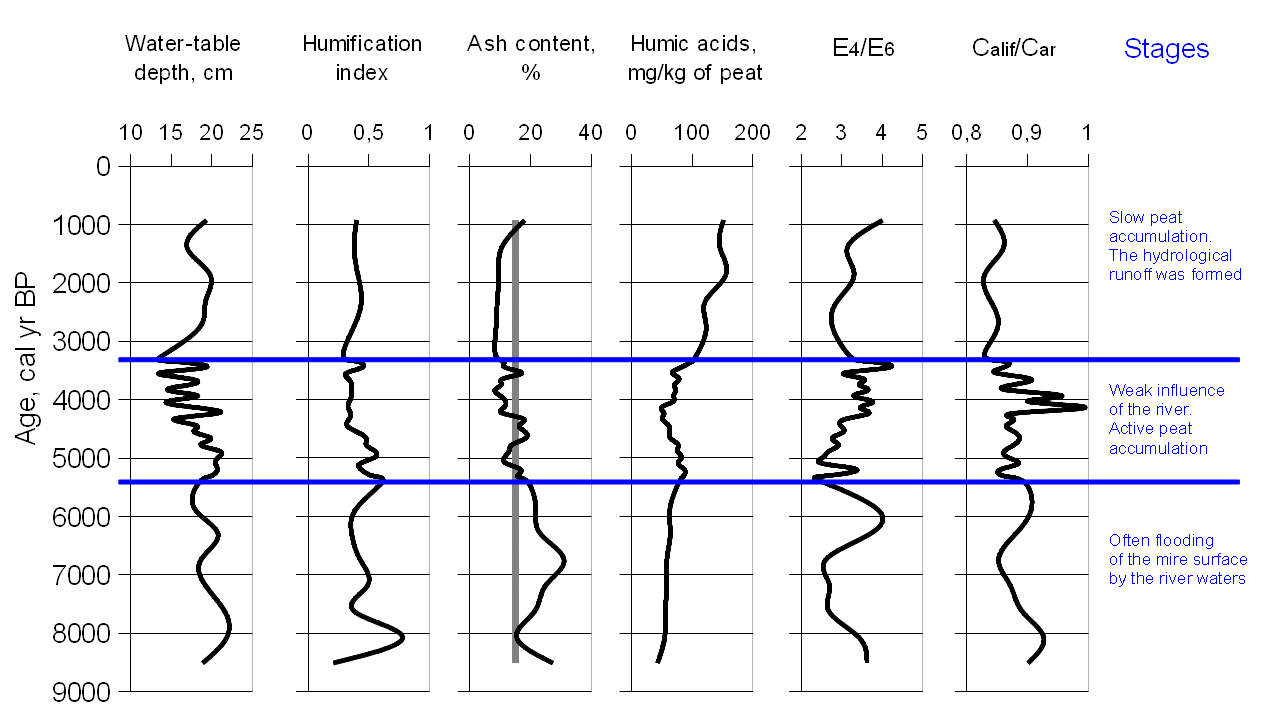
- The influence of the river was greatest at the first stage of development of the eutrophic peatland.
- Highly mineralized groundwater significantly inhibits oligotrophication of the mire.
- Synchronous surface wetness changes in various mires are the results of climate fluctuations in the Holocene.
- Climate change is evident in the dynamics of peat humification and reconstructed water-table depth.
The paleoecological study of the peat deposit of the floodplain terrace eutrophic peatland located in south of the taiga zone of Western Siberia was carried out. The work is based on an integrated approach including the following methods: radiocarbon dating, macrofossil analysis, rhizopod analysis, humification degree and physico-chemical characteristics of humic acids of peats. Comparison of the results obtained by different methods allowed us to reconstruct the history of the development of floodplain terrace eutrophic peatland determined by the local hydrological, geomorphological and geochemical conditions on the background of climate change. At the first stage of development, the peatland was often flooded by the river, which provided additional introduction of mineral matters and followed by increased ash content of peat. Then the influence of the river had weakened, and the growth of the peat deposit was more determined by the factors of endogenous peat bog formation and the level of surface hydrological runoff. This led to the formation of peats with normal ash content; hygrophytic grasses were replaced with sedges and hypnum plant assemblages. The eutrophic peatland showed the highest sensitivity to climate change over the last 8500 years. It is confirmed with synchronous variations of surface wetness in different bogs of the study area.
Regional Geographical Problems
- In comparison with the neighboring regions and Russia as a whole, Volgograd Oblast has a significant potential for further use of its surface and groundwater resources.
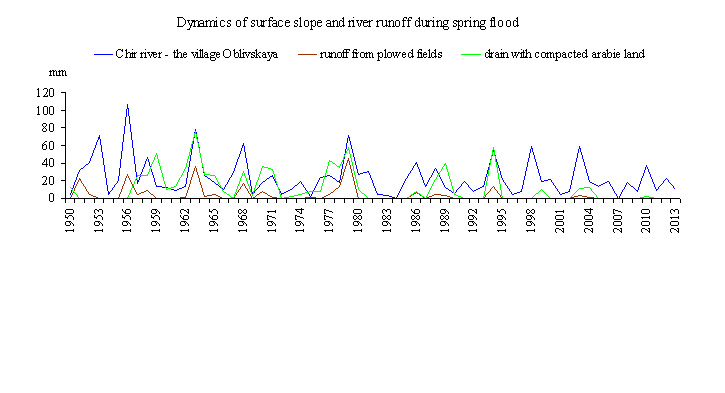
- Under the influence of climatic factors, surface slope runoff is reducing.
- Due to the increased by 25–40% infiltration of atmospheric precipitation during the cold season (including the spring flood period), the soil moisture resources increase before the beginning of the growing season, which creates a potential for higher yields.
- Structural changes in water balance of the river watersheds contribute to the reduction of unevenness of the intraannual distribution of river flow.
Methodological approaches to assessing the water potential of the territory, its resource and ecological components, are proposed and tested on the case study of Volgograd oblast. Data are presented on its main elements: local river runoff and inflow of river water from neighboring areas, surface and groundwater resources. The size and structure of its water-resource potential of Volgograd oblast is estimated. The current trends in the influence of water management, agricultural activities and climate on water resources are revealed. A hydroecological assessment of their changes is given. It is shown that the oblast has a significant potential for further use of its water resources, if not to consider the need in irrigation of the neighboring Astrakhan and Rostov oblasts by the Volga and Don waters. Taking into account the low quality of river waters, the water potential of Volgograd oblast can be judged as largely exhausted. The specifics of the current hydroecological situation are characterized.
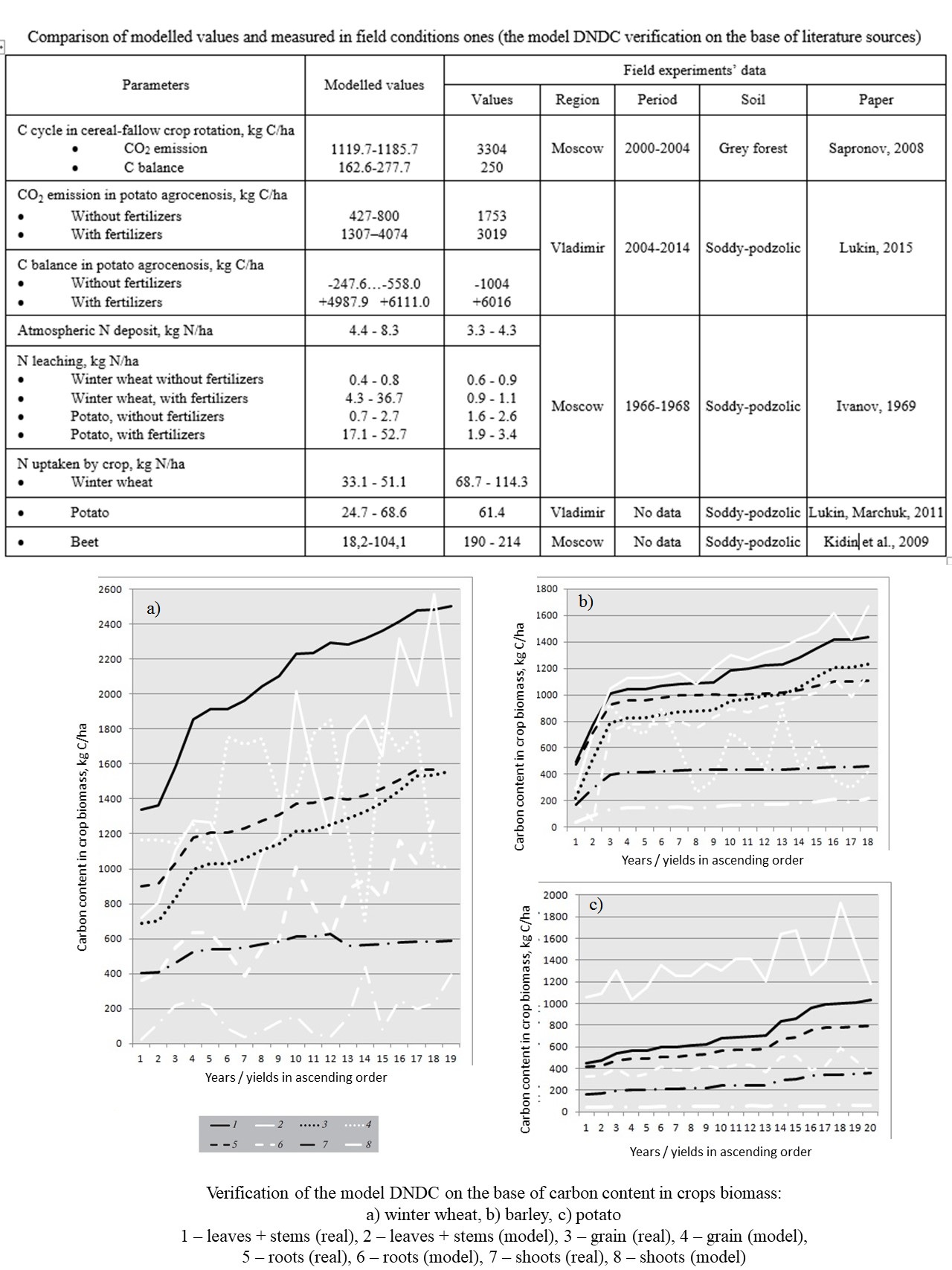
- The DNDC (DeNitrification-DeComposition) model represents correctly values of CO2 emission and other components of carbon biogeochemical cycle.
- The modeled values of nitrogen cycle components in the Non-Chernozem zone differ from the measured ones.
- The DNDC model properly predicts patterns of crops biomass formation and its input into soil.
- A method for the DNDC model verification on the base of carbon content in crop biomass is presented.
- In Russia the best model’s results were obtained for the grain crops.
The approbation of the DNDC (DeNitrification-DeComposition) model was done. The aim of research was to evaluate an opportunity of model using for analysis of carbon and nitrogen exchange and greenhouse gases dynamics in agroecosystems of arable soils in the Central Non-Chernozem zone in Russia. The verification of the model on the base of literature data detected that, as a rule, in arable Non-Chernozem soils modeled values of carbon biogeochemical cycle components and carbon dioxide emission are no higher than real ones. For nitrogen uptake by crops and nitrogen, leaching under fertilizing conditions, there was not conformity between modeled results and field experiments data. The method of verification on the base of carbon content in crop biomass calculation was presented. DNDC is good for spring grain crops modeling, but often the values of plant biomass are decreased by model plant biomass.
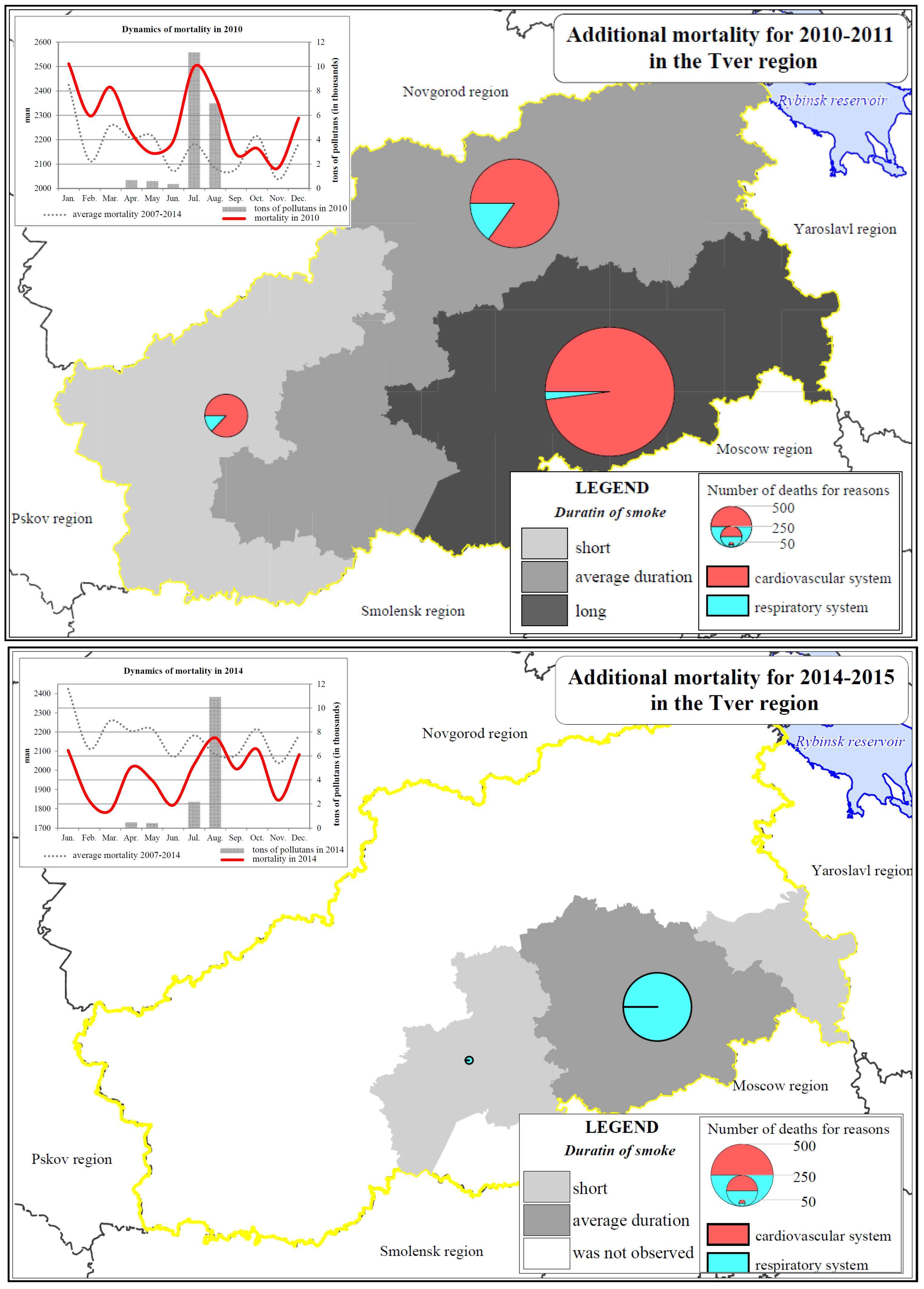
- Forest fires increased mortality in the Tver region in 2010 and 2014.
- The fires increased mortality from the pathology of circulatory system, while the delayed effects of smoke resulted in increased number of deaths from the respiratory diseases in the following year.
- In the year of the fire exposure, mortality increased by 1–4%, and in the subsequent year by 1%.
History of Geography and Historical Geography
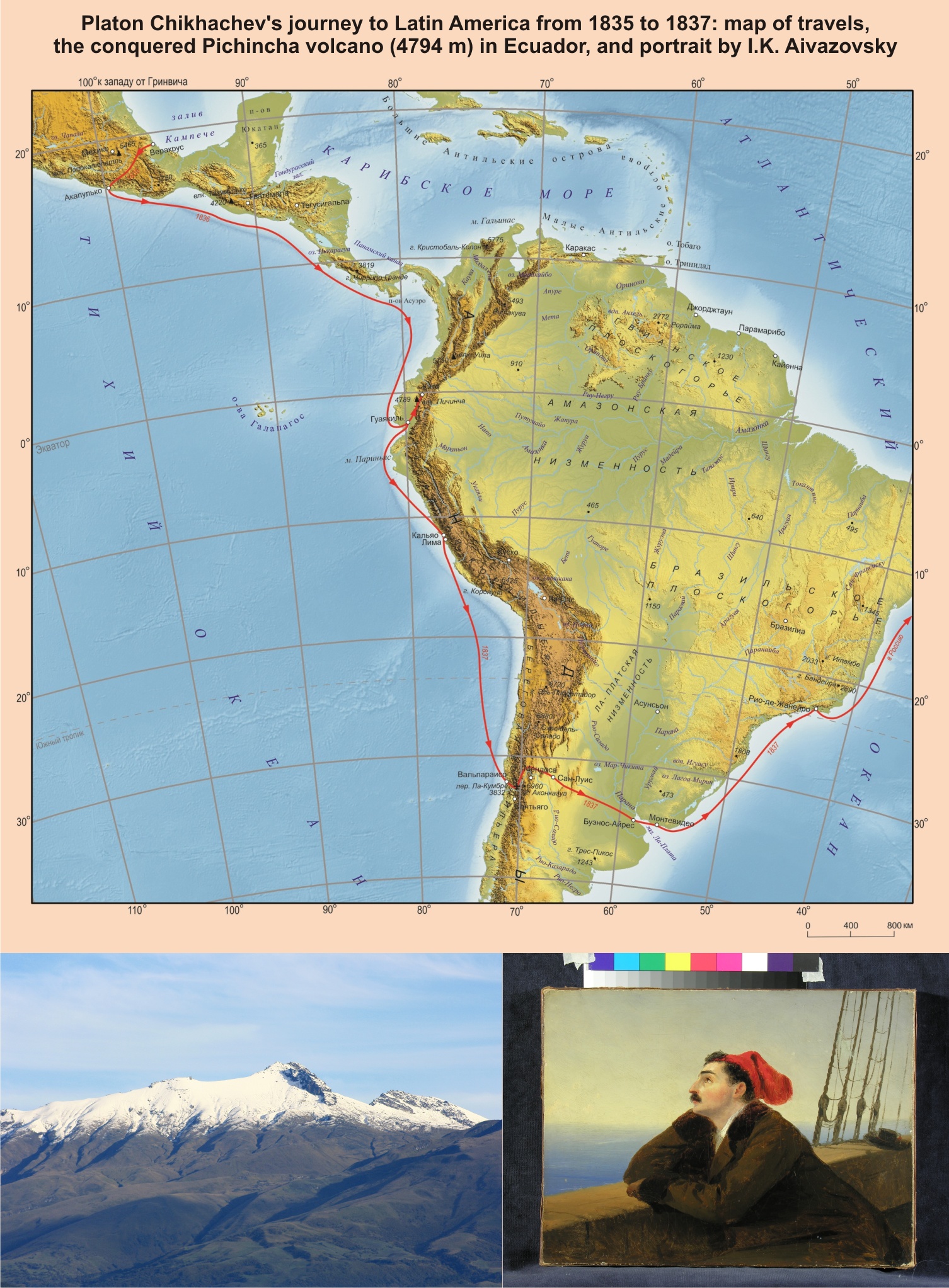
- Platon Chikhachev is an outstanding geographer of the first half of the 19th century, one of the initiators and founding members of the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.
- For the first time the Chikhachev’s portrait by I.K Aivazovsky, kept for many years in a private collection, is published in scientific literature.
- The little-known facts of his travels are presented: crossing Mexico from the East coast to the West coast, crossing the Andes from Santiago to Mendoza and then the pampas of Argentina to Buenos Aires on horseback, ascent of the Pichincha volcano in Ecuador, the world’s first ascent of the Aneto peak (Pyrenees), participation in the Khiva expedition.
The way of life of the outstanding Russian geographer, traveler, humanist, one of the initiators of creation and the founders of the Russian Imperial geographical society, honorary member of the St. Petersburg Mineralogical Society and one of the first successful climbers in the world Platon Aleksandrovich Chikhachev was bright, full of discoveries, adventures, tragic episodes, public recognition and oblivion. He was born in 1812, was on military service from 1828 to 1831, traveled to North and South America in 1835–1837, and in 1840– 1845 to Europe and Russia, where he took part in the creation of the Imperial geographical society. At the very beginning of his life, being a 16-years-old officer, he participated in 3 wars, later in the famous Khiva campaign of 1839–1840, and in the Crimean war in 1855. In 1856, he married and went to Europe. He died in Versailles in 1892, and was buried in Nice at the Russian cemetery. After retiring from the army in 1833, he devoted himself to travelling to Europe and the New World. He became the first Russian who in the early 19th century crossed Mexico from the East to the western coast of the Pacific Ocean; made a dangerous crossing on horseback in South America – from Chile through the Andes and pampas of Argentina reached Buenos Aires. Platon Chikhachev first conquered the mountain peaks – Pichincha volcano in Ecuador and Aneto peak, the highest point of the Pyrenees, and became one of the first climbers in Europe. The article adds new data to the well-known features of the biography of a guard officer, scientist, and traveler: little-known episodes of life, including those related to his stay in the homeland; it is clarified the sequence of events and the chronicle of the life of a scientist and traveler based on primary sources. The facts of Platon Chikhachev’s routes were specified, and contribution to the development of national and world geography was assessed.
Surveys and reviews
- The book In Focus of Heritage was prepared for the 25th anniversary of the Likhatchev Russian Research Institute for Cultural and Natural Heritage and the jubilee of its founder, geographer Yu.A. Vedenin.
- The content of the book accurately reflects the process of development of the original ‘Russian cultural landscape’ concept.
- Creative atmosphere of the Heritage Institute determined openness of its achievements for practitioners, working in the field of nature conservation, recreation and ecotourism.
Jubilees
ISSN 2658-6975 (Online)